더보기
▣오늘의 주요 키워드▣
- 다중열 서브쿼리
- SCALAR SUBQUERY
>복습 문제
[문제74] 년도,분기별 급여의 총액을 구하세요.
년도 1분기 2분기 3분기 4분기
-------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
2001 17000
2002 36808 21008 11000
2003 35000 8000 3500
2004 40700 14300 17000 14000
2005 86900 16800 60800 33400
2006 69400 20400 14200 17100
2007 36600 20200 2500 35600
2008 46900 12300
1)가로
select *
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'q') season, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for season in (1 "1분기",2 "2분기",3 "3분기",4 "4분기"));
2)세로
select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'), to_char(hire_date, 'q'), sum(salary)
from employees
group by to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'), to_char(hire_date, 'q');
3-1)최종
select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') "년도",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'q'),1,salary)),0) "1분기",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'q'),2,salary)),0) "2분기",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'q'),3,salary)),0) "3분기",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'q'),4,salary)),0) "4분기"
from employees
group by to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy')
order by 1;
3-2)최종(pivot)
select *
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') "년도", to_char(hire_date, 'q') quarter, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for quarter in (1 "1분기",2 "2분기",3 "3분기",4 "4분기"))
order by 1;
>null값 0으로 치환
select 년도, nvl("1분기", 0) "1분기", nvl("2분기", 0) "2분기", nvl("3분기", 0) "3분기", nvl("4분기", 0) "4분기"
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') "년도", to_char(hire_date, 'q') quarter, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for quarter in (1 "1분기",2 "2분기",3 "3분기",4 "4분기"))
order by 1;

>unpivot 가로를 다시 세로로 표현
select *
from (select 년도, nvl("1분기", 0) "1분기", nvl("2분기", 0) "2분기", nvl("3분기", 0) "3분기", nvl("4분기", 0) "4분기"
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') "년도", to_char(hire_date, 'q') quarter, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for quarter in (1 "1분기",2 "2분기",3 "3분기",4 "4분기"))
order by 1)
unpivot(급여총액 for 분기 in ("1분기", "2분기", "3분기", "4분기"));
>include nulls(unpivot에서 생략된 null값들을 보여주는 기능)
select *
from (select *
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') "년도", to_char(hire_date, 'q') quarter, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for quarter in (1 "1분기",2 "2분기",3 "3분기",4 "4분기"))
order by 1)
unpivot include nulls(급여총액 for 분기 in ("1분기", "2분기", "3분기", "4분기"));
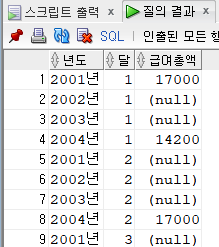
[문제75] 달(월)별 년도별 급여 총액을 아래 결과처럼 출력해주세요.
달 2001년 2002년 2003년 2004년
-------- -------- ------- ------- -------
01
02
...
12
1) decode함수
select to_char(hire_date, 'mm') 달,
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'),'2001', salary)),0) "2001년",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'),'2002', salary)),0) "2002년",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'),'2003', salary)),0) "2003년",
nvl(sum(decode(to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy'),'2004', salary)),0) "2004년"
from employees
group by to_char(hire_date, 'mm');
2) pivot
select 달, nvl("2001년", 0) "2001년", nvl("2002년", 0) "2002년", nvl("2003년", 0) "2003년", nvl("2004년", 0) "2004년"
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'mm') 달, to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') year, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for year in ('2001' "2001년", '2002' "2002년", '2003' "2003년", '2004' "2004년"))
order by 1;
3) unpivot
select *
from (select *
from (select to_char(hire_date, 'mm') 달, to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') year, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for year in ('2001' "2001년", '2002' "2002년", '2003' "2003년", '2004' "2004년"))
order by 1)
unpivot include nulls(급여총액 for 년도 in ("2001년", "2002년", "2003년", "2004년"));
--년도랑 달이랑 자리바꾸고 싶을 때
select 년도, 달, 급여총액
from (select *
from (select to_number(to_char(hire_date, 'mm')) 달, to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') year, salary
from employees)
pivot (sum(salary) for year in ('2001' "2001년", '2002' "2002년", '2003' "2003년", '2004' "2004년"))
order by 1)
unpivot include nulls(급여총액 for 년도 in ("2001년", "2002년", "2003년", "2004년"));

★다중열 서브쿼리
★다중열 서브쿼리
-- 쌍비교
select *
from employees
where(manager_id, department_id) in (select manager_id, department_id
from employees
where first_name = 'John');
-- 비쌍비교
select *
from employees
where manager_id in (select manager_id
from employees
where first_name = 'John')
and department_id in (select department_id
from employees
where first_name = 'John');
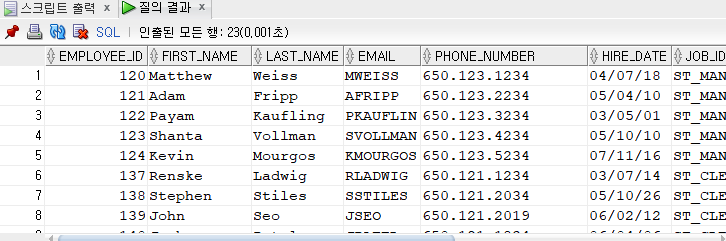
-쌍비교와 비쌍비교를 언뜻 보면 똑같아보이지만 추출된 행이 다른 것을 알 수 있다. 왜 그런지 알아보자
쌍비교는 manager_id, department_id를 한번에 쌍으로 잡고 비교하는데 비쌍비교는 manager_id별로 동작하고 또department_id로도 동작하므로 수행되는 과정이 다르다.(똑같이 나올 수도 있음)
[문제76] commission_pct null이 아닌 사원들의 department_id, salary 일치하는 사원들의 정보를 출력해주세요.
1)쌍비교
select *
from employees
where (department_id, salary) in (select department_id, salary
from employees
where commission_pct is not null);
2)비쌍비교
select *
from employees
where department_id in (select department_id
from employees
where commission_pct is not null)
and salary in (select salary
from employees
where commission_pct is not null);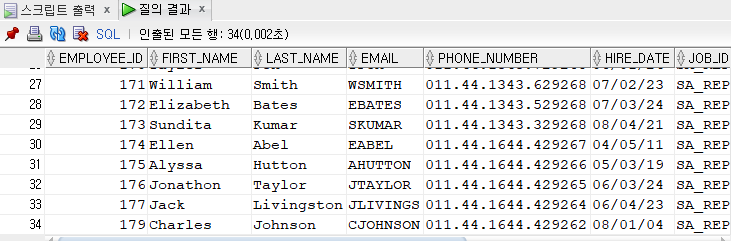
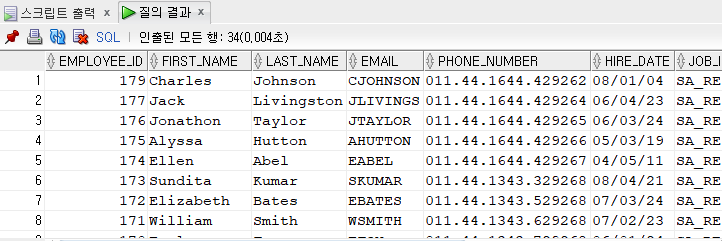
[문제77] location_id가 1700 위치에 있는 사원들의 salary, commission_pct가 일치하는 사원들의 정보를 출력해주세요.
1) 쌍비교
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE (salary, nvl(commission_pct,0)) in (SELECT e.salary, nvl(e.commission_pct,0)
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id=d.department_id
AND d.location_id=1700);
2) 비쌍비교
SELECT *
FROM employees
WHERE salary in (SELECT e.salary
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id=d.department_id
AND d.location_id=1700)
AND nvl(commission_pct,0) in (SELECT nvl(e.commission_pct,0)
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id=d.department_id
AND d.location_id=1700);

★scalar subquery
- 한 행에서 정확히 하나의 열값만 반환하는 쿼리(단일컬럼, 단일값만 리턴해야한다)
- 동일한 입력값이 들어오면 수행 횟수를 최소화 할 수 있는 로직을 구현한다.
- query execution cache 기능이 수행된다.
- 키값이 없는 데이터가 입력되면 null값으로 리턴한다.(outer join 기법처럼 결과가 출력된다.)
>scalar subquery
select employee_id, department_id, (select department_name --query execution cache(메모리)
from departments
where department_id = e.department_id)
from employees e
order by 2;
>일반 join(outer join)
select e.employee_id, e.department_id, d.department_id, d.department_name
from employees e, departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+);
[문제78] 부서이름별 급여의 총액, 평균을 구하세요.
1) 일반적인 형식 --조인을 다 하고 그룹핑
select department_name, sum(salary), avg(salary)
from employees e, departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
group by department_name
order by 1;2) inline view 이용 --축소를 한 다음 조인
select d.department_name, e.sum_sal, e.avg_sal
from (select department_id, sum(salary) sum_sal, avg(salary) avg_sal
from employees
group by department_id) e, departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+)
order by 1;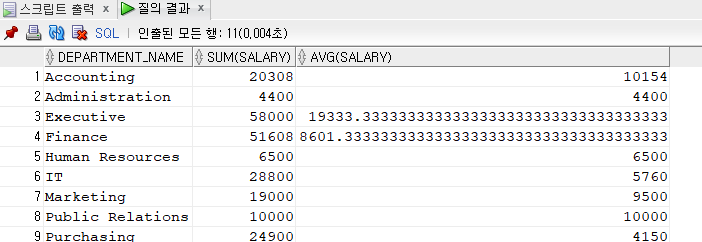
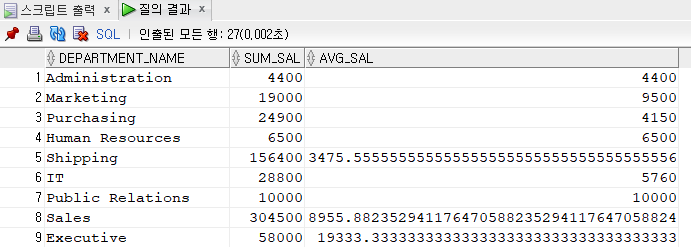
3) scalar subquery 이용 --조인을 안 하고 조인한 것처럼 나오는 장점, but 단일값만 사용가능
①
select department_name, (select sum(salary)
from employees
where department_id = d.department_id) sum_sal,
(select avg(salary)
from employees
where department_id = d.department_id) avg_sal
from departments d;
--------------------------------
②
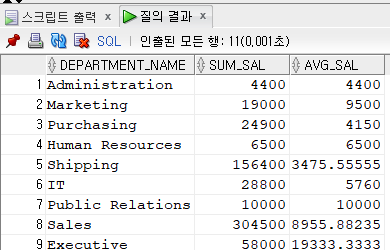
select department_name, substr(sal,1,10) sum_sal, substr(sal,11) avg_sal --자릿수를 고정해놓았기에 원하는 자리까지 추출
from(select department_name, (select lpad(sum(salary),10) ||lpad(avg(salary),10) --자리수를 고정해놓음
from employees
where department_id = d.department_id) sal
from departments d)
where sal is not null;
>① 코드의 단점은 employees테이블을 두 번들어가서 효율이 떨어진다.
따라서 ② 코드처럼 연결연산자와 lpad 함수를 사용하여 자리수를 고정해놓고 substr로 추출하게 되면
간단히 employees 테이블을 한 번만 들어가게 되어서 효율성이 높아진다.
[문제79] 사원들의 last_name, salary, grade_level을 출력해주세요.
1) 조인
select e.last_name, e.salary, j.grade_level
from employees e join job_grades j
on e.salary between j.lowest_sal and j.highest_sal;
2) scalar subquery --캐시기능이 돌아가는 장점이 있다.
select last_name, salary, (select grade_level
from job_grades
where e.salary between lowest_sal and highest_sal) grade_level
from employees e
order by 2;
[문제80] 사원들의 employee_id, last_name을 출력을 하는데 단 department_name을 기준으로 정렬해주세요.
1)outer join
select e.employee_id, e.last_name
from employees e, departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id(+)
order by d.department_name;
2)order by(scalar subquery)
SELECT employee_id, last_name
FROM employees e
ORDER BY (SELECT department_name
FROM departments
WHERE department_id = e.department_id) asc; --다른 테이블을 기준으로 정렬할 때!!
- ORDER BY 절에 SCALAR SUBQUERY를 사용할 수 있다.
'SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 12.30 오늘의 공부 (0) | 2021.12.30 |
|---|---|
| 12.29 오늘의 공부 (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| 12.27 오늘의 공부 (0) | 2021.12.27 |
| 12.24 오늘의 공부 (0) | 2021.12.24 |
| 12.23 오늘의 공부 (0) | 2021.12.23 |